Prerequisites
To begin with this guide, make sure you have the following:
- An Ubuntu 24.04 server.
- A non-root user with administrator privileges.
- A domain name pointed to a server IP address.
Installing dependencies
TYPO3 is an open-source content management system written in PHP and supports databases such as MySQL/MariaDB and PostgreSQL. In this section, you'll install dependencies for TYPO3, which includes the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP), Composer as PHP dependency management, and GraphicsMagick for image processing.
Before you start, update your Ubuntu package index with the command below.
sudo apt update
Now install package dependencies for TYPO3 CMS with the following 'apt install' command. With this command, you will install dependencies such as the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP), Composer as PHP package manager, Git, and GraphicsMagick for automatic image processing.
sudo apt install apache2 mariadb-server composer graphicsmagick php php-common php-mysql libapache2-mod-php php-gd php-curl php-json php-xmlrpc php-intl php-gmagick php-bcmath php-zip php-apcu php-mbstring php-fileinfo php-xml php-soapType Y to proceed with the installation.
When the installation is complete, verify the status for both Apache and MariaDB services, and then check the PHP, Composer, and GraphicsMagick versions.
Verify the Apache service status with the command below. You should get the output of the Apache service as 'enabled' and 'active (running)'.
sudo systemctl is-enabled apache2 sudo systemctl status apache2

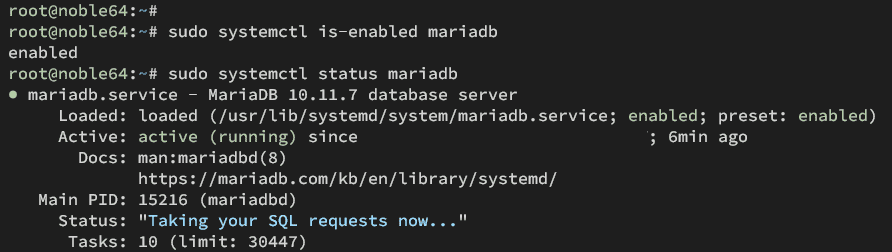
Next, check the MariaDB service status using the following command. The output should be similar to Apache, you'll see the MariaDB server is 'enabled' and 'active (running)'.
sudo systemctl is-enabled mariadb sudo systemctl status mariadb
gm version

Configuring PHP
To install TYPO3, you must change the default PHP configuration file 'php.ini'. You need to edit the 'php.ini' file for both Apache and PHP CLI, then change some default configurations for TYPO3 installation.
Edit the 'php.ini' file for both Apache and PHP CLI with the following nano editor command.
sudo vi /etc/php/8.3/apache2/php.ini sudo vi /etc/php/8.3/cli/php.ini
Change the default configuration with the following. Make sure to adjust the 'memory_limit' and 'date.timezone' options with your server environment.
date.timezone = Europe/Amsterdam memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 240 max_input_vars = 1500 post_max_size = 50M upload_max_filesize = 50M
Save the file and exit.
Now run the command below to restart the Apache service and apply your changes on PHP.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
After that, run the following command to create a new 'info.php' file in the '/var/www/html' directory.
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > /var/www/html/info.php
Configuring MariaDB server
Now that you've configured PHP, you need to secure the MariaDB server, and then create a new database and user for TYPO3. In this section, you'll secure MariaDB using the 'mariadb-secure-installation' utility and create a new database and user from the command line.
Secure your MariaDB server installation by executing the 'mariadb-secure-installation' command below.
sudo mariadb-secure-installation
Now, you will be prompted to configure the MariaDB server. Enter Y to accept the default setting or n to reject it.
- The default MariaDB installation comes without a password, press ENTER when prompted for the password.
- Now input Y to set up the MariaDB root password. Then, type the new password for MariaDB and repeat the password.
- Input Y to remove the anonymous user from your MariaDB installation.
- Input Y again when prompted to disable the remote login for the MariaDB root user.
- Input Y to remove the default database test from your MariaDB.
- Lastly, input Y to reload table privileges and apply new changes.
After you've configured the MariaDB server, log in to the MariaDB with the following command. Input your MariaDB root password when prompted.
sudo mariadb -u root -p
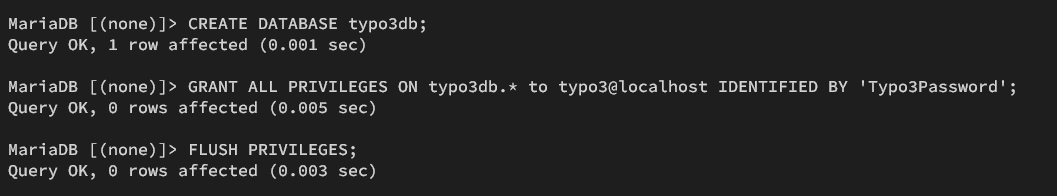
Now run the following queries to create a new database, 'typo3db', and a new user, 'typo3', with the password 'Typo3Password'. Change details database information as you need.
CREATE DATABASE typo3db; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON typo3db.* to typo3@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'Typo3Password!!!'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Next, run the query below to check privileges for user 'typo3'. This will ensure that user 'typo3' can access the database 'typo3db' for your TYPO3 CMS installation.
SHOW GRANTS FOR typo3@localhost;
The output below shows you that user 'typo3' can access the database 'typo3db'.
Lastly, type quit to exit from the MariaDB server.

Downloading TYPO3 via Composer
There are multiple ways to install and download the TYPO3 source code. Now you will set up the TYPO3 installation directory, and then download TYPO3 using Composer (PHP dependencies management).
First, run the following command to create new directories for Composer cache and configuration, and the TYPO3 installation directory '/var/www/typo3'.
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/{.cache,.config,typo3}Now run the command below to change the ownership of the above directories to user 'www-data', and then enable read and write access to the '/var/www/typo3' directory.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/{.cache,.config,typo3}
sudo chmod u+rw /var/www/typo3Next, go to the '/var/www/typo3' directory and install TYPO3 CMS with the 'composer' command below. In this example, you will install the latest version of TYPO3 CMS v12 to your Ubuntu server.
cd /var/www/typo3 sudo -u www-data composer create-project typo3/cms-base-distribution:^12 .
You can see below the TYPO3 CMS download and installation process:
Setting up TYPO3 via the command line
After downloading the TYPO3 CMS source code, you will configure the TYPO3 installation using the command line. You can also set up the TYPO3 installation using a web browser, but now you'll be configuring the TYPO3 CMS installation from your terminal.
To configure TYPO3 CMS installation via command, run the following:
./vendor/bin/typo3 setup
You will be prompted with the following configurations:
- Type apache as the web server.
- Type mysqli as the database driver.
- Input details of your MariaDB user, password, port, and host that will be used for TYPO3 CMS.
- Type typo3db as the database name.
- Type your administrator user, password, and email address for TYPO3 CMS. Your password must contain a special character at least one.
- For the project name, leave it as default.
- Press ENTER when asked to create the basic site.
If your installation is successful, you will see an output 'Congratulations - TYPO3 Setup is done'.
Lastly, re-run the following command to change the ownership of the '/var/www/typo3' directory to user 'www-data'.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/typo3
Setting up Apache virtual host
Now that you've configured TYPO3 from the terminal, let's move on to configure the Apache virtual host for your TYP3 installation. So make sure that you've prepared your domain name.
First, activate the Apache 'rewrite' module with the following command.
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Then create a new virtual host file '/etc/apache2/sites-available/typo3.conf' using the following nano editor command.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/typo3.conf
Insert the following configuration and make sure to change the ServerName option with your TYPO3 CMS domain name. In this example, TYPO3 CMS will be running on the domain 'howtoforge.local'.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin riley.wortman@umatillacounty.gov
DocumentRoot /var/www/typo3/public
ServerName www-test
<Directory /var/www/typo3/public/>
Options FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
<Directory /var/www/typo3/public/>
RewriteEngine on
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^(.*) index.php [PT,L]
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>a2enmod rewriteNow run the command below to activate the 'typo3.conf' virtual host file and verify your Apache syntax. The output 'Syntax OK' will be displayed, if you have proper Apache syntax.
sudo a2ensite typo3.conf sudo apachectl configtest
Lastly, restart the Apache service with the command below to apply your TYPO3 CMS virtual host. When executed, your TYPO3 CMS installation will be ready.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Securing TYPO3 CMS with HTTPS
In this section, you'll secure TYPO3 CMS with HTTPS using Certbot and Letsencrypt. Certbot will be used for generating SSL/TLS certificates from Letsencrypt. Also, you will be using the Certbot Apache plugin to set up automatic HTTPS on your virtual hosts.
Install Certbot and the Certbot APache plugin with the command below. Type Y to proceed with the installation.
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache
After the installation, run the 'certbot' command below to generate SSL/TLS certificates for your TYPO3 CMS domain name. So make sure to change the domain name and email address with your information.
sudo certbot --apache --agree-tos --redirect --hsts --staple-ocsp --email alice@howtoforge.local -d howtoforge.local
When the process is finished, your TYPO3 CMS will secured with HTTPS automatically. Your SSL/TLS certificates are available in the '/etc/letsencrypt/live/domain.com' directory.
Accessing TYPO3
Visit the TYPO3 CMS login page at https://howtoforge.local/typo3 using your preferred web browser. If your installation is successful, you should get the TYPO3 CMS login page.
Input your admin user and password, then click Login to confirm.
le end
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article